SoilEnrich Cow Dung Manure





SoilEnrich Cow Dung Manure
Soilenrich cow dung manure, also known as cow manure or cow dung fertilizer, is a nutrient-rich organic material derived from the excrement of cows. It has been used for centuries as a natural fertilizer in agriculture due to its ability to improve soil structure and fertility.
Composition
- Nutrients: Cow dung manure is rich in essential nutrients, including nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), which are vital for plant growth. It also contains micronutrients such as calcium, magnesium, and sulfur.
- Organic Matter: High in organic matter, cow manure helps enhance soil structure, aeration, and water retention capabilities.
- Beneficial Microorganisms: Contains beneficial microorganisms that promote healthy soil microbial activity, aiding in the decomposition of organic matter and nutrient cycling.
Benefits of Soilenrich cow dung Manure as an Organic Fertilizer in Agriculture
Soilenrich cow dung manure offers numerous advantages for agricultural use, contributing to healthier crops and sustainable farming practices. Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Soil Fertility Improvement
- Nutrient-Rich: Cow dung manure is packed with essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and various micronutrients that are vital for plant growth and development.
- Organic Matter: It adds a significant amount of organic matter to the soil, which helps improve soil structure and fertility.
2. Enhanced Soil Structure
- Soil Aeration: The organic matter in cow manure improves soil aeration, which is crucial for root development and overall plant health.
- Water Retention: Improved soil structure enhances the soil's ability to retain water, reducing the need for frequent irrigation.
3. Microbial Activity Boost
- Beneficial Microorganisms: Cow dung manure is rich in beneficial microorganisms that help breaks down organic matter and release nutrients slowly, ensuring a steady supply for plants.
- Soil Health: Increased microbial activity promotes a healthy soil ecosystem, which can suppress soil-borne diseases and pests.
4. Natural and Eco-Friendly
- Chemical-Free: As an organic fertilizer, cow dung manure reduces the dependence on chemical fertilizers, which can have harmful environmental effects.
- Sustainable Farming: Using cow manure supports sustainable farming practices by recycling waste and reducing agricultural pollution.
5. Plant Growth and Yield
- Balanced Nutrition: The balanced nutrients in cow manure support robust plant growth, leading to higher yields and better-quality crops.
- Slow-Release Fertilizer: Cow dung manure acts as a slow-release fertilizer, providing a consistent nutrient supply over time and reducing the risk of nutrient leaching.
6. Cost-Effective
- Affordable: For farmers with access to cattle, cow dung manure is a costeffective fertilizer option compared to synthetic fertilizers.
- Local Resource: Utilizing locally available cow manure can reduce transportation costs and carbon footprint.
7. Soil pH Regulation
- pH Balance: Cow manure can help neutralize acidic soils, creating a more favorable environment for plant growth.
8. Weed Control
- Weed Suppression: When composted properly, cow dung manure can help suppress weed growth by adding organic matter that competes with weeds for space and nutrients.
Application Tips
- Composting: Compost cow dung before application to reduce pathogens and stabilize nutrients. Proper composting also minimizes odor and kills weed seeds.
- Incorporation: Mix the composted manure into the soil before planting or use it as a top dressing around existing plants.
- Dosage: Adjust the application rate based on soil fertility tests and specific crop requirements to avoid over-fertilization.
Nutrient Content
1. Macronutrients
- Nitrogen (N): Approximately 0.5% to 1.5%
- Phosphorus (P, as P2O5): Approximately 0.2% to 0.8%
- Potassium (K, as K2O): Approximately 0.4% to 1.0%
2. Secondary Nutrients
- Calcium (Ca)
- Magnesium (Mg)
- Sulfur (S)
Micronutrients
- Iron (Fe)
- Manganese (Mn)
- Zinc (Zn)
- Copper (Cu)
- Boron (B)
- Molybdenum (Mo)
Organic Matter
- Carbon (C)
- Humic substances: Enhance soil structure and water retention
- Cellulose and hemicelluloses: Fibrous materials that decompose slowly
- Lignin: A complex organic polymer that contributes to soil organic matter
Microbial Content
- Beneficial Microorganisms: Promote soil health and nutrient cycling, including bacteria, fungi, and actinomycetes. Moisture Content
- Water: Fresh cow dung typically contains about 80% moisture. After composting, the moisture content is reduced to around 30-50%. pH Level
- Cow dung manure typically has a neutral to slightly alkaline pH, ranging from 6.5 to 8.0.
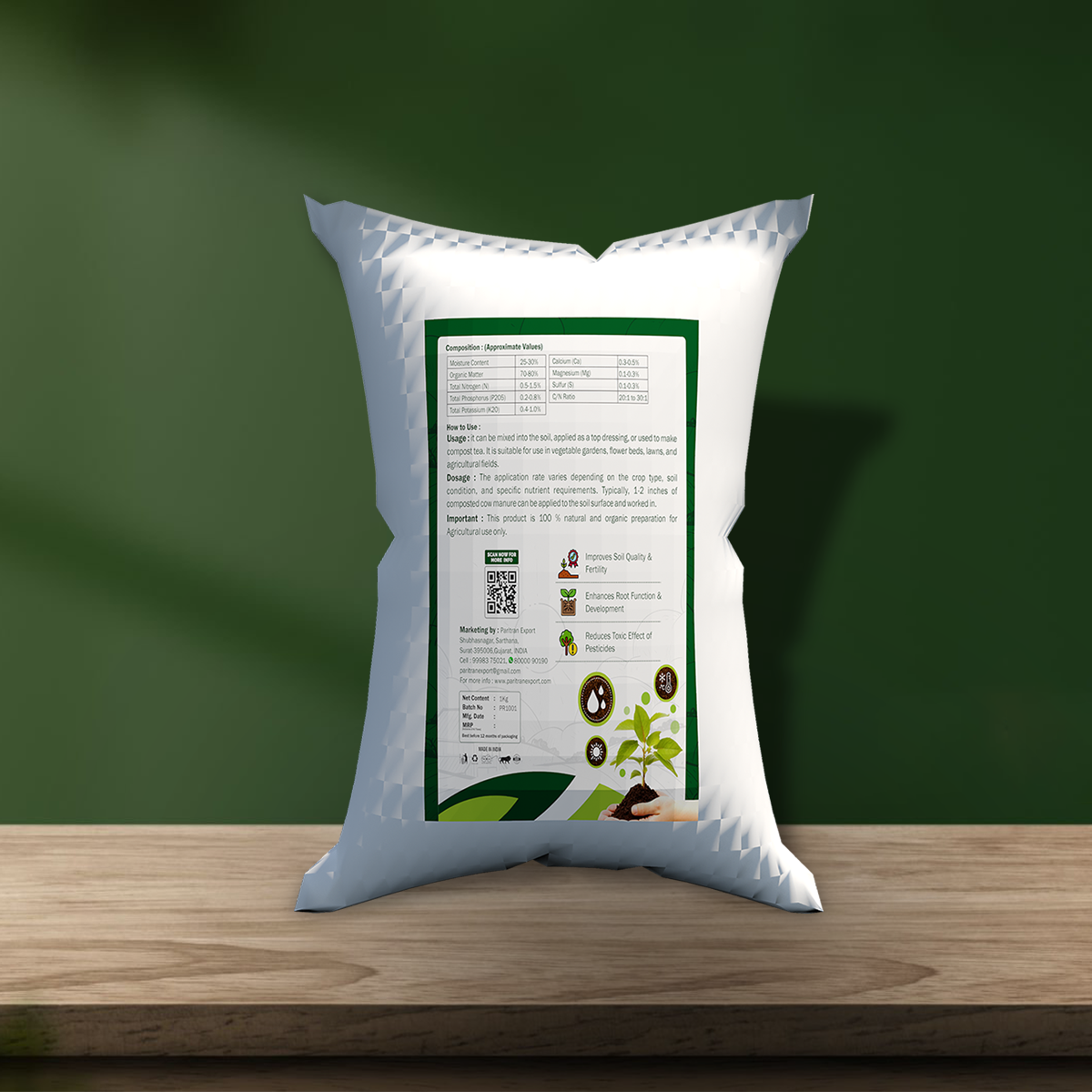
Typical Composition (Approximate Values)
- Dry Matter: 20-25%
- Organic Matter: 70-80% of dry matter
- Total Nitrogen (N): 0.5-1.5%
- Total Phosphorus (P2O5): 0.2-0.8%
- Total Potassium (K2O): 0.4-1.0%
- Calcium (Ca): 0.3-0.5%
- Magnesium (Mg): 0.1-0.3%
- Sulfur (S): 0.1-0.3%
- C/N Ratio: 20:1 to 30:1
Overall, using Soilenrich cow dung manure as a fertilizer can help improve plant health and productivity while promoting sustainable agriculture practices. However, it is important to use high-quality cow dung manure from a reputable source and to follow proper application rates to avoid any potential contamination or negative effects on plant growth.
